Abstract
Introduction
Obinutuzumab (G), a humanized type II glycoengineered anti-CD20 therapeutic monoclonal antibody (mAb), exhibits target mediated drug disposition, a situation where pharmacokinetics (PK) is considered as a surrogate marker of CD20 occupancy. The recommended dose and schedule of G in the treatment of patients (pts) with B cell malignancies was determined based on safety, efficacy, and PK profile to ensure full target saturation throughout the entire dosing period (Cartron et al , 2016). Understanding the relationships between clinical outcome and G exposure is confounded by the underlying relationships between exposure, tumor burden (which changes over time), CD20 target density and disease biology. In this analysis, we evaluated the sources of variability including exposure to G in outcome amongst pts with previously untreated (1L), advanced follicular lymphoma (FL) who received G-based immunochemotherapy in the GALLIUM trial (NCT01332968).
Material and Methods
The GALLIUM trial is described elsewhere (Marcus R et al , ASH 2016). Serum G concentrations collected during Induction and Maintenance in 408 pts with 1L, G-treated FL were analyzed and included in a population PK analysis. For each patient, predicted Cmean values were computed from the PK model, as the ratio of cumulative area under the curve (AUC) over the duration of the Induction period. Tertiles of Cmean (low, medium, high) were used to reflect variability in exposure among pts.
A multivariate regression analysis (Cox analysis) was used to investigate the effect of various factors such as exposure (Cmean), and baseline patient and disease characteristics on PFS (e.g FLIPI score, ECOG status, bone marrow involvement, presence of bulky disease (>7cm), polymorphism of Fcg receptor IIb/IIc, Ann Arbor stage).
In this analysis, we also specifically evaluated the relationship between body weight (BW) and exposure and the correlation with PFS using a univariate semi-parametric Cox proportional hazard model of BW.
Results:
Among pts with available PK data (n=408) solely those who received at least 50% of the planned induction cycles of G (ie ≥4 cycles of G-CHOP/CVP (n=189 pts), ≥3 cycles of G-Benda (n=212 pts); total n = 401) were included in the PFS analysis.
In GALLIUM, similarly to most mAbs, the main factors associated with lower G exposure in FL pts were higher BW, but also high tumor burden at baseline (BSIZ), and male gender (Gibiansky et al , CPT Pharmacometrics Syst Pharmacol., 2014). In addition, age, serum albumin level and chemotherapy backbone were also influential (E. Gibiansky et al , PAGE, 2016; Table I).
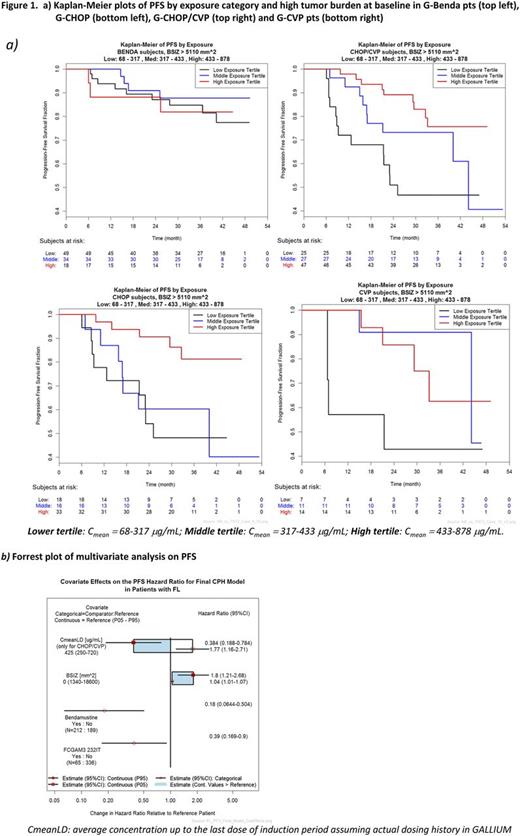
A Cox analysis showed that PFS was negatively impacted by high BSIZ and presence of the Fcγ polymorphism IIa/IIb 232TT single nucleotide polymorphism. In pts treated with G-Benda, the PFS benefit was similar across G exposure categories. In pts treated with G-CHOP (n=130) or G-CVP (n=59), G exposure seems to be associated with PFS outcome, especially in pts with high BSIZ. Sample size was smaller compared to G-Benda pts, therefore G-CHOP and G-CVP pts were grouped in the analysis (Fig 1).
Kaplan-Meier (KM) plots of PFS by baseline BW categories (≤90 Kg, >90kg) were performed (HR = 1.52 with 95% CI: 0.91, 2.54) (Fig. 2). A separation in PFS was observed between pts with BW £ 90 kg and > 90 kg; however, the 95% CI was large and included the value of 1. This indicates that the apparent visual separation in the KM curves of PFS between the BW categories is not statistically significant.
Conclusion
Exposure to G is highly variable among pts; however this variability does not correlate with clinical outcome in pts treated with G-Benda. In these pts differences in exposure cannot be considered as the primary determinant of inferior clinical outcome. Intrinsic patient and disease characteristics (e.g., tumor burden) are likely relevant contributors to differences in PFS. PET and Minimal Residual Disease are also prognostic for outcome and additional results will be provided at the time of presentation. In pts treated with G-CHOP or G-CVP, lower exposure is associated with shorter PFS; however it remains unknown whether exposure is a cause or rather a consequence of poorer prognosis (Matts Kagedal et al , PAGE 2017). Sample size was smaller and the comparative efficacy of Benda vs CHOP/CVP is under debate.
Jamois: Roche: Employment, Other: GALLIUM was sponsored by F. Hoffmann-La Roche Ltd.. Gibiansky: Roche: Consultancy. Gibiansky: Roche: Consultancy. Buchheit: Roche: Employment. Baumlin: Roche: Employment. Sahin: Roche: Employment, Equity Ownership. Cartron: Sanofi, BMS, Jansen, celgene, Roche, Gilead: Equity Ownership; Celgene: Consultancy, Employment; Roche: Consultancy, Equity Ownership, Honoraria, Research Funding. Marcus: Roche: Consultancy, Honoraria, Other: Travel support, Speakers Bureau; Celgene: Other: Support for meeting attendance . Strefford: Roche: Research Funding. Meneses-Lorente: Roche Products Ltd: Employment. Frey: Roche: Employment. Fingerle-Rowson: F. Hoffmann-La Roche Ltd: Employment, Equity Ownership.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.
This icon denotes a clinically relevant abstract

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal